In the global distributed photovoltaic (PV) market, rooftops of residential and low-rise buildings remain one of the most important application scenarios. Tile roofs solar mounting systems appear widely in residential architecture and account for a significant share of installations across Europe, Japan, Australia, and other regions.
Tile roofs involve complex structural layouts, waterproofing methods, and load transfer paths. These characteristics prevent PV installations from relying on generic rooftop mounting solutions. Instead, engineers must design systems specifically for different tile types and roof structures.
In this context, solar mounting systems with proven tile roof experience play a critical role in ensuring smooth project execution and long-term operational reliability.
1. What Is a Tile Roof Solar Mounting System?
A tile roof solar mounting system provides an engineered solution for securely installing photovoltaic modules on tiled roofs. The system not only supports the modules but also integrates safely with the roof structure.
Rather than combining metal components at random, engineers design this system as an integrated solution. It accounts for structural mechanics, material performance, waterproofing requirements, and architectural aesthetics.
By addressing these factors together, tile roof mounting systems improve installation safety and long-term system stability.
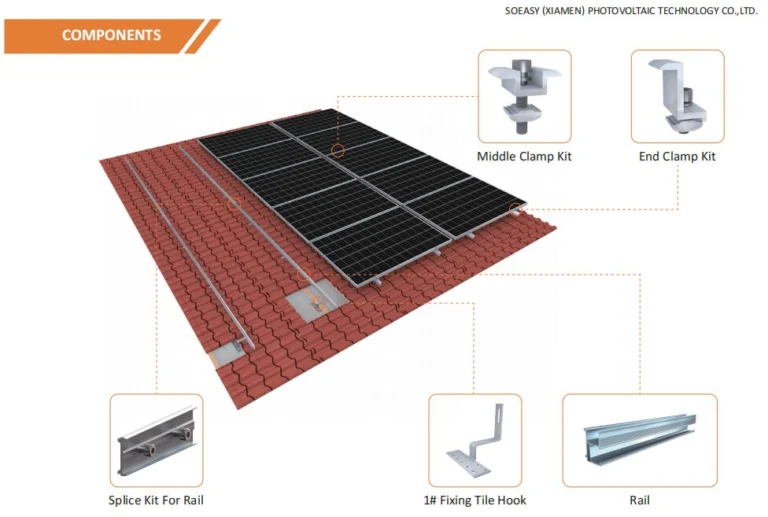
2. Core Components of a Tile Roof Solar Mounting System
Roof Attachment System (The Critical Interface)
The roof attachment system connects the PV installation directly to the building structure. It forms the most critical part of a tile roof mounting solution.
- Dedicated Tile Hooks
Engineers design tile hooks according to specific tile profiles. These hooks connect directly to load-bearing elements such as rafters or trusses while minimizing stress on the tiles. - Waterproofing System
The system uses a multi-layer waterproofing approach. Designers typically combine EPDM sealing pads, specialized sealants, and drainage channels to manage water at penetration points. - Height Adjustment Mechanisms
Adjustable components compensate for variations in tile thickness and roof unevenness. This design ensures a level installation plane for the mounting rails.
Support Structure System
The support structure carries module loads and transfers them to the roof attachment points.
- Rails
Manufacturers commonly use aluminum alloys such as 6005-T5 or 6063-T6 for mounting rails. Anodized surface treatment improves corrosion resistance while maintaining strength and low weight. - Connectors
Clamp-based or bolt-based connectors secure the modules to the rails. Their design provides sufficient clamping force without creating stress concentration on the module glass. - Mid Clamps and End Clamps
Mid clamps and end clamps perform different functions. End clamps offer higher uplift resistance to withstand wind loads.
Safety and Protection Measures
- Grounding and Lightning Protection
Dedicated grounding clips connect the mounting system to the building’s lightning protection network. Most standards require grounding resistance to remain below 4 ohms. - Anti-Loosening Design
Installers use anti-loosening washers or self-locking nuts on all fasteners to prevent vibration-related failures. - Galvanic Corrosion Prevention
Insulating pads separate dissimilar metals and reduce the risk of electrochemical corrosion.
3. Common Tile Roof Types and Mounting Considerations
Different tile materials and profiles require different mounting approaches.
| Tile Type | Recommended Mounting Solution | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Clay Tile | Embedded or custom tile hook | Tiles fracture easily; drilling requires proper tools and techniques |
| Concrete Tile | Universal adjustable hook system | Designers must consider tile thickness tolerances |
| Slate Tile | Side-clamp mounting system | Installers avoid penetrating slate and use layered fixation |
| Glazed Tile | Customized tile hook | Smooth surfaces require additional anti-slip features |
Aesthetic and Architectural Considerations
- Color Matching
Anodized aluminum components support RAL color customization. Common selections include dark gray (RAL 7016) and dark brown (RAL 8017). - Low-Profile Design
Designers typically maintain a clearance of 50–70 mm between the module frame and the tile surface. This spacing supports ventilation while limiting visual impact. - Alignment with Roof Geometry
Installers align rails with roof ridges or eaves to preserve clean architectural lines.
4. How to Select a Tile Roof Solar Mounting Solution
Step 1: Roof Assessment
A detailed roof inspection should precede system selection.
- Structural Condition
Inspectors check wooden structures for rot and aging. They examine steel structures for corrosion. - Tile Integrity
Inspectors sample tiles across the roof. If damage exceeds 5%, the project should include roof repairs before installation. - Drainage Performance
Installers verify that gutters and downspouts allow unobstructed water flow.
Step 2: Material Selection
Aluminum mounting systems offer a balance of lightweight construction, corrosion resistance, and cost efficiency. These systems perform well in most climates.
Stainless steel systems provide higher mechanical strength and stronger corrosion resistance. Engineers often specify them for coastal zones and heavily polluted industrial environments.
As a general guideline, engineers recommend stainless steel systems within 500 meters of coastal areas. In other locations, anodized aluminum systems usually deliver the best balance between performance and cost.
Step 3: Climate-Adaptive Design
For High-Wind Regions
- Increase the number of end clamps, with at least six per module
- Add anti-uplift bracing where necessary
- Reduce tile hook spacing at roof edges from 1.2 m to approximately 0.8 m
For Snow-Heavy Regions
- Increase module tilt angles to promote snow shedding
- Install snow guards to control snow movement
- Account for uneven snow loads during structural calculations
Tile Hook–Based Solutions
The long-term reliability of tile roof PV projects depends not only on module performance but also on how well the mounting system integrates with the roof structure. In tile roof installations, tile hooks form the critical interface between the PV system and the building.
Tile hook design directly influences structural safety, waterproofing performance, and installation efficiency.
Drawing on extensive experience with tile profiles and roof structures, SOEASY provides a comprehensive range of Tile Hook solutions. These solutions support common clay tiles, concrete tiles, and various irregular roof profiles.
Optimized structural design and standardized interfaces allow Soeasy Solar Tile Hooks to transfer loads reliably while minimizing stress on the tiles. At the same time, the system maintains effective roof waterproofing.
When combined with matched rail systems and standardized connection components, Soeasy Solar’s tile roof mounting solutions support structural integrity, simplify installation, and promote long-term operational stability for residential and small commercial PV projects.
As distributed solar continues to expand worldwide, selecting a mature and adaptable Tile Hook solution—starting from the roof structure itself—creates a solid foundation for long-term value in tile roof PV installations.
 English
English 







